总览
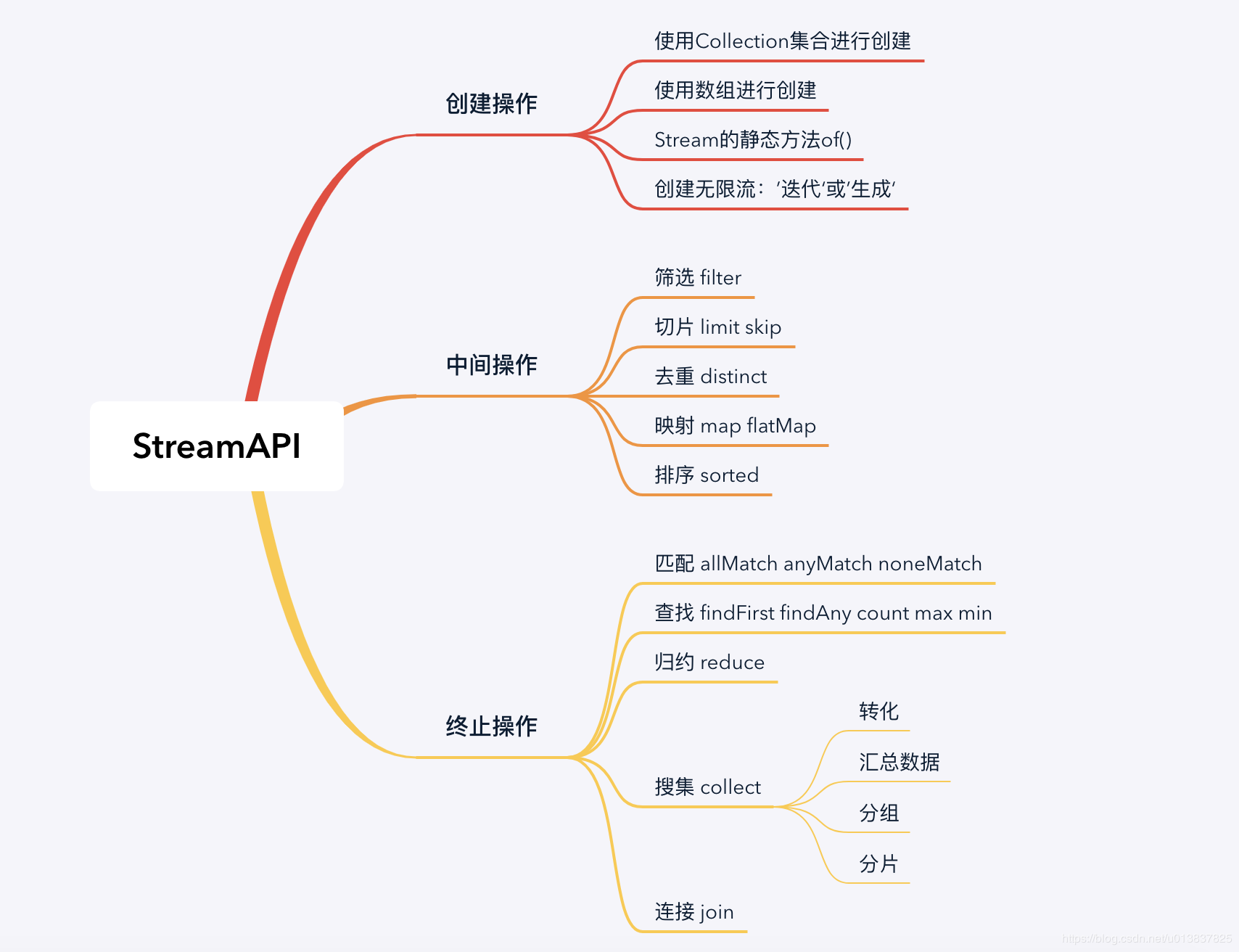
1.介绍
- Stream创建 -> 中间操作 -> 终止操作
流一旦使用终止操作,就不能再进行中间操作
- Java8 特性
- 与 函数式接口 配合使用
- 与 Optional 配合使用
- 惰性求值
多个中间操作可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水 线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理!而在终止操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”。
2.Stream 的创建
2.1 使用 Collection 集合进行创建
default Stream
stream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}
default Stream
parallelStream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);}
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<Integer>();
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
collection.add(3);
collection.add(4);
// 串行流
Stream<Integer> stream1 = collection.stream();
// 并行流
Stream<Integer> stream2 = collection.parallelStream();
2.2 使用数组进行创建
public static
Stream stream(T[] array)
public static
Stream stream(T[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive)
public static IntStream stream(int[] array) …
public static LongStream stream(long[] array) …
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array) …
Integer[] array = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3, 4};
Stream<Integer> stream1 = Arrays.stream(array);
2.3 Stream 的静态方法 of()
public static
Stream of(T... values)
Stream<Integer> stream1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4);
2.4 创建无限流 ’迭代‘ 或 ’生成‘
public static
Stream iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator f)
public static
Stream generate(Supplier s)
Stream<Integer> stream1 = Stream.iterate(1, (t) -> t + 2);
Stream<Double> stream1 = Stream.generate(() -> new Random().nextInt(100));
2.5 其他
public static
Stream concat(Stream<? extends T> a, Stream<? extends T> b)
3.Stream 的中间操作
3.1 筛选 filter
Stream
filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
Stream<Student> stream2 = stream1.filter((t) -> {
if (t.getAge() >= 18) {
return true;
}
return false;
});
3.2 切片 limit skip
Stream
limit(long maxSize); 截取前N个元素
Stream
skip(long n); 忽略前N个元素
3.3 去重 distinct
Stream
distinct();
以对象的 hashCode() 和 equals() 来判定是否是同一个元素
3.4 映射 map flatMap
Stream map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);
IntStream mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper);
LongStream mapToLong(ToLongFunction<? super T> mapper);
DoubleStream mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T> mapper);
Stream flatMap(Function<? super T, ? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper);
…
Stream<Student> stream2 = stream1.map((o) -> {
if (o.getName().contains("敏感词汇")) {
o.setName(o.getName().replaceAll("敏感词汇","*"));
}
return o;
});
Stream<String> stream2 = stream1.map(Student::getName);
对比 flatMap 和 map 的区别: flatMap会将结果拼装成一个整体
public void test7() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "gq");
Stream<Stream<Character>> stream
= list.stream().map(StreamAPIOperrateDemo::stringToCharacter);
Stream<Character> stream2
= list.stream().flatMap(StreamAPIOperrateDemo::stringToCharacter);
stream.forEach((sm) -> sm.forEach(System.out::print));
//
System.out.println();
stream2.forEach(System.out::print);
//
}
private static Stream<Character> stringToCharacter(String string) {
List<Character> characterList = new ArrayList<>();
char[] chars = string.toCharArray();
for (Character ch : chars) {
characterList.add(ch);
}
return characterList.stream();
}
3.5 排序 sorted
Stream
sorted();
前提:T 实现 Comparable 接口
Stream
sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
//Stream<Student> stream2 = stream1.sorted();
//Stream<Student> stream2 = stream1.sorted(new StudentComparator());
//Stream<Student> stream2 = stream1.sorted((s1, s2) -> s1.getAge() - s2.getAge());
Stream<Student> stream2 = stream1.sorted((s1, s2) -> Integer.compare(s1.getAge(),s2.getAge()));
// 推荐
Stream<Student> stream3 = stream1.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getAge));
// 逆序
Stream<Student> stream4 = stream1.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getAge).reversed());
4.Stream 的终止操作
4.1 匹配 allMatch anyMatch noneMatch
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
检查是否匹配所有元素
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
检查是否至少匹配一个元素
boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
检查是否没有匹配的元素
4.2 查找 findFirst findAny count max min
Optional
findFirst();
返回第一个元素
Optional
findAny();
返回当前流中的任意元素
long count();
返回流中元素的总个数
Optional
max(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
返回流中最大值
Optional<Integer> maxAge = stream1.distinct().map(Student::getAge).max(Integer::compare);
Optional
min(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
返回流中最小值
4.3 归约 reduce
T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator
accumulator);
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Integer sum = list.stream().reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println(sum);
Optional
reduce(BinaryOperator accumulator);
U reduce(U identity, BiFunction<U, ? super T, U> accumulator, BinaryOperator combiner);
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("June", "Kmde", "Kang", "Zhan", "Gui");
Optional<String> result = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x + "_" + y);
System.out.println(result.get());
Integer sum = stream1.distinct().map(Student::getAge).reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
Optional<Integer> sum = stream1.distinct().map(Student::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
4.4 搜集 collect
R collect(Supplier supplier, BiConsumer<R, ? super T> accumulator, BiConsumer<R, R> combiner);
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);
可以借助Collectors工具类进行构建Collector对象;
4.4.1 转化
可以转化成List、Set、Map …
List<String> names = stream1.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
Set<String> names = stream1.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<String> names = stream1.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
Map<Integer, String> names = stream1.distinct().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getId, Student::getName));
4.4.2 汇总数据
汇总 总量、总数值、平均值、最大最小值…
Long count = stream1.collect(Collectors.counting());
Double sum = stream1.collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Student::getHeight));
Double avg = stream1.collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Student::getHeight));
Optional<Student> optionalStudent = stream1.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparingDouble(Student::getHeight)));
// 汇总统计
DoubleSummaryStatistics sum = stream1.collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Student::getHeight));
System.out.println(sum.getCount());
System.out.println(sum.getSum());
System.out.println(sum.getAverage());
System.out.println(sum.getMax());
System.out.println(sum.getMin());
4.4.3 分组
Map<Integer, List<Student>> stuMap = stream1.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge));
stuMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("age:" + key);
value.forEach(System.out::println);
});
// ----
Map<Integer, Map<String, List<Student>>> stuMap = stream1.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge, Collectors.groupingBy(t -> {
if (t.getHeight() >= 1.80) {
return "挺高";
} else if (t.getHeight() <= 1.60) {
return "偏矮";
} else {
return "正常";
}
})));
stuMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("age:" + key);
value.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("height" + k);
v.forEach(System.out::println);
});
});
4.4.4 分片
Map<Boolean, List<Student>> booleanListMap = stream1.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(t -> t.getAge() >= 18));
booleanListMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("age:" + key);
value.forEach(System.out::println);
});
4.4.5 连接 join
String names = stream1.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(",", "<Start>", "<End>"));