关于 PIPE
查看手册
man 7 pipe
Broken pipe问题
python3 -c 'while True: print(1)' | head -n 1
> python3 -c 'while True: print(1)' | head -n 1
1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
BrokenPipeError: [Errno 32] Broken pipe
Exception ignored in: <_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>
BrokenPipeError: [Errno 32] Broken pipe
(yes; echo $? > /dev/stderr) | head -n 1
> (yes; echo $? > /dev/stderr) | head -n 1
y
141
关于 _start
void main(){
}
void _start(){
main();
// handle
systemcall(SYS_exit, 0);
}
gcc -Wall -g -ffreestanding -nostdlib -static sh.c -o sh
glibc
libc是Standard C library的简称; libc库提供C语言中所使用的宏,类型定义,字符串操作函数,数学计算函数以及输入输出函数等。 我们在Linux操作系统下所说的libc即glibc, glibc是类Unix操作系统中使用最广泛的libc库,它的全称是GNU C Library。
glibc是GNU工具链的关键组件,用于和二进制工具和编译器一起使用,为目标架构生成用户空间应用程序。 当从源码进行构建时,一些Linux程序可能需要链接到某个特定版本的glibc。
ldd –version
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
- https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/
- https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/libc/
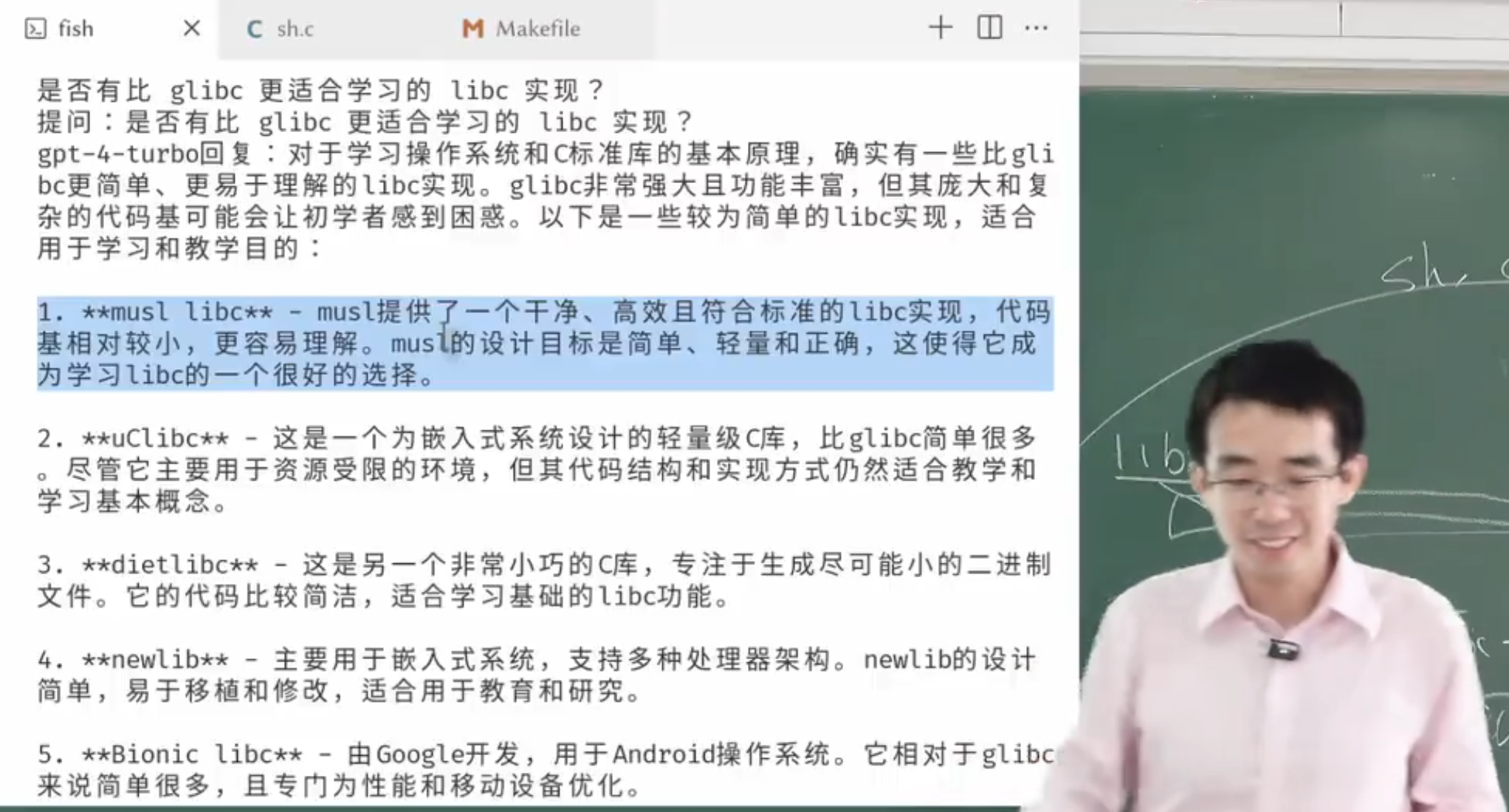
musl libc
musl is an implementation of the C standard library built on top of the Linux system call API
https://musl.libc.org/
which mush-gcc
cat (which mush-gcc)
Freestanding 环境
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/freestanding
- https://cplusplus.com/reference/cinttypes/
FILE
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *p = fopen("1.txt","r");
printf("*p=%p\n", p);
if(!p){
perror("not open");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
env
#include <stdio.h>
extern char ** environ;
int main() {
for(char **env=environ;*env;env++){
printf("%s\n", *env);
}
return 0;
}
等效于
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[], char *envp[]) {
for(char **env=envp;*env;env++){
printf("%s\n", *env);
}
return 0;
}
System V Application Binary Interface
https://jyywiki.cn/OS/manuals/sysv-abi.pdf
给libc的实现者写的,如果想要实现自己的 libc 实现,则遵守这个标准的话,代码的运行效果将与其他系统的运行效果一致.
动态内存管理
利用 mmap 系统调用,自己实现 malloc 和 free 函数
脱离 workload 做优化就是耍流氓
去哪里找 workload? 当然是 paper 了
Mimalloc: free list sharding in action (APLAS’19) or
Thinking, Fast and Slow by Daniel Kahneman
- Fast path (System I) 性能极好、并行度极高、覆盖大部分情况 ; 但有小概率会失败
- Slow path (System II) 不在乎那么快, 但不会失败
malloc: Fast Path 设计
- 线程都事先瓜分一些 “领地” (thread-local allocation buffer)
- 默认从自己的领地里分配
- 如果自己的领地不足,就从全局的池子里借一点
分配: Segregated List (Slab)
每个 slab 里的每个对象都一样大
每个线程拥有每个对象大小的 slab
fast path → 立即在线程本地分配完成
slow path → pgalloc()
动态内存管理小内存:Segregated List (cont'd)
分配: Slab
问题被简化了
一个内存页被分配成大小是 2^𝑘的分配单元
每个分配单元里塞个指针,就是 free list 了
(uintptr_t)p & 0xfff 就可以得到对应的 slab
头部可以存放一些 metadata,例如自旋锁
回收:直接归还到 slab 中
注意这可能是另一个线程持有的 slab
需要 per-slab 锁 (小心数据竞争)